Although children have a higher risk of developing ear infections, adults can also experience them. The onset of ear infections is usually rapid and symptoms can be very painful. In addition to pain, infections can also affect hearing because sound cannot get through the fluid. Ear infections usually occur when the eustachian tube is blocked either by allergies, or by bacterial or viral infection and become clogged with fluid and mucus.
What is an Ear Infection?
There are two types of ear infections that affect the middle ear: the most common type of ear infection is when viruses or bacteria get into the middle ear, the space behind the eardrum. The other affects the middle ear and is called otitis media with effusion (OME). This occurs when fluid builds up over time in the middle ear without being infected.
If the outer ear canal becomes infected, this is commonly referred to as “swimmer’s ear”.
Who Can Get Ear Infections?
Both children and adults can get ear infections but children are more likely to be diagnosed with an infection. Risk factors for ear infections include:
- Age - children ages 6 months to 2 years are more susceptible to ear infections because their eustachian tubes and immune systems are still developing. Their tubes are shorter, narrower and more horizontal than adults’ tubes. Learn more about pediatric ENT conditions.
- Upper respiratory tract infections- infections to the immune system can cause ear infections in children and adults.
- Child care- children in classrooms or group settings are more likely to get sick and develop ear infections as they are exposed to more people and more germs.
- Allergies- ear infections are more common in the fall and winter than in the warmer months. People with seasonal allergies have an increased risk of ear infections when pollen counts are high.
- Nasal polyps- enlarged structures in your ears, nose or throat such as nasal polyps, adenoids and turbinates can also increase risk of ear infections
- Cotton swabs- avoid using q-tips or cotton swabs in the ear as they can increase chances for infection.
What Are Ear Infection Symptoms?
Ear pain is one of the most common symptoms associated with ear infections (especially middle ear infections), but other symptoms include:
- Fever
- Trouble eating or drinking
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Fluid draining from the ear
- Hearing loss
- Loss of balance
- Trouble sleeping
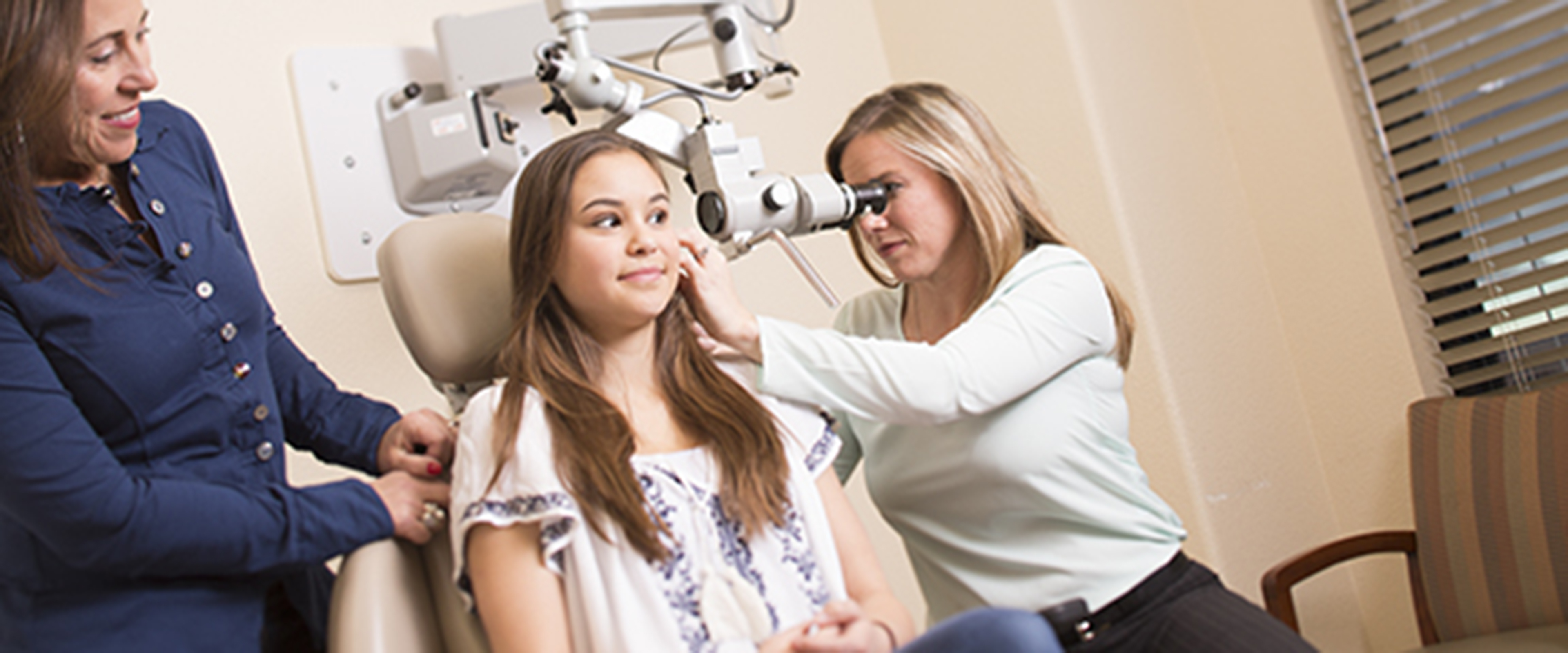
Symptoms of an ear infection can indicate a number of conditions so it is best to get a diagnosis as soon as possible. Make an appointment today. During your appointment, your doctor will look at your outer ear and eardrum with an otoscope to properly diagnose your condition.
If your child has a fever over 102 degrees, discharge from the ear or symptoms lasting more than two days, contact a healthcare professional immediately.
Chronic ear infections can cause long-term or permanent damage to the ear. These chronic infections develop when the infected fluid behind the eardrum does not go away. This can happen from an infection that does not properly heal or with repeated infections over time.
How To Treat an Ear Infection
Depending on what type of ear infection you are diagnosed with, your treatment options may vary. Some ear infections require an antibiotic while others are treated with ear drops and over-the-counter pain relievers. Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial ear infections. It’s important to ask your healthcare provider about what medications are safe to take.
Some ear infections (OME) go away on their own and may not be impacted by the use of antibiotics.
How To Prevent Ear Infections
There are many ways to prevent ear infections in both children and adults. Flu vaccines are provided annually and can help eustachian tube problems and thus prevent bacteria from growing in the fluid in your ear. We also recommend that you keep foreign objects out of your ears such as cotton swabs, bobby pins and more as these objects can bruise or puncture the ear canal, leaving them susceptible to infection.
Adults should also limit exposure to cigarette smoke or secondhand smoke as this can lead to more colds and infections in the ear.
There are additional preventative steps that can be taken to avoid early childhood ear infections. Breastfeeding infants for at least 12 months after birth has proven to be beneficial in preventing ear infections in babies. It's also important to keep children up to date on their vaccinations.
Book an Appointment
To meet with our highly-skilled team at Sierra Nevada Ear Nose & Throat, please give us a call to schedule an appointment at one of our three locations.